At a Glance: Budget Session 2023 (Part-1)
17 February 2023
The Budget Session of Parliament commenced on 31st January and is scheduled to conclude on 6th April. The session adjourned on 14th February for a month-long recess till 13th March. Below are curated highlights from the Question Hour and Zero Hour during the first leg of the session (between 31st January to 14th February 2023).
Highlights from Question Hour and Zero Hour
Rural Development
● Under the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) scheme, a total of ₹ 2.24 lakh crore has been released so far to more than 11 crore farmers, as on 7 February 2023.
● Under the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), launched in 2016, a total of 38 crore farmer applications have been enrolled and over 12.37 crore (provisional) farmer applicants have received claims in the past six years. Claims of over ₹ 1,30,015 crore (provisional) have been paid to them, as on 7 February 2023.
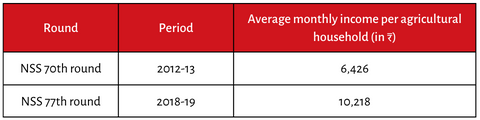
● The change in average monthly income of agricultural households, as per to the Situation Assessment Survey (SAS) of agricultural households by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO), is as follows:
● Under Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana- Gramin (PMAY-G), a total of 1.3 crore houses have been sanctioned to the eligible citizens and 97.7 lakh houses have been constructed between 2019-20 and 2021-22. The overall target of PMAY-G is set at 2.95 crore houses by 31 March, 2024. The beneficiaries under PMAY-G are identified based on the Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) 2011 database and finalized Awaas+ survey list.
(Download our 2023 Budget Brief on the Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana- Gramin to know the status and progress of the scheme)
● As per the Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) Management Information System (MIS), out of total rural households, about 57.12% rural households across the country have a tap water connection, as on 31 January, 2023. A total of 7 states and UTs reported 100% coverage, namely Gujarat, Telangana, Haryana, Goa, Puducherry, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and Dadra and Nagar Haveli, and Daman and Diu.
(To know more about the trends in allocations, releases, and coverage under the scheme, download our 2023 Budget Brief on Jal Jeevan Mission)
Education
● Under the Right to Education (RTE) Act, the Pupil-Teacher Ratio (PTR) norms for primary and upper primary level are 30:1 and 35:1, respectively. As per UDISE 2021-22 (Provisional), at the national level, the PTR for government primary and upper primary schools are 28:1 and 24:1, respectively.
However, several states have higher PTR than the norms under the RTE Act. Among others, Bihar (60:1), Delhi (40:1), Jharkhand (33:1), and Haryana (32:1) had high PTR for primary level. Only Delhi (39:1) and Jharkhand (38:1) had a PTR higher than the RTE norms at the upper primary level.
● Under the Samagra Shiksha scheme, GoI has approved a ‘Rejuvenation of Basic Infrastructure’ project for 1.20 lakh government schools across the country. Under the project, interventions such as major and minor repairs, functional toilets, electricity connections, functional drinking water facility, and boundary walls are covered, with an overall budget estimate of ₹ 4,590 crore.
(Download our 2023 Budget Brief on Samagra Siksha to know the status and progress of the scheme)
● Under the PM POSHAN Scheme, previously known as the National Scheme for Mid-Day Meals in schools (MDM), the overall cost per student is ₹ 11.38 and ₹ 16.25 for primary and upper primary levels, respectively.
(To know more about the trends in allocations, releases, and coverage under the scheme, download our 2023 Budget Brief on PM POSHAN)
Health
● Under the Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), over 50 crore citizens (or 10.74 crores households) have been covered with a health insurance cover.
As on 31 January 2023, a total of 1.56 lakh Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centers (AB-HWCs) are operational across the country.
As on 2 February 2023, a total of 23.07 crore Ayushman Cards have been issued to verified eligible citizens. Under Ayushman Bharat scheme, more than ₹ 4.34 crore hospital admissions worth ₹ 51,749 crore have been authorised through a network of 26,049 empanelled healthcare providers including 14,200 private hospitals.
(Download our 2023 brief on Ayushman Bharat to know the status and progress of the scheme.)
● According to Rural Health Statistics (RHS) 2021-22, the total number of functional Primary Healthcare Centres (PHCs) in the country stands at 24,935. Out of these, 11,250 PHCs i.e. 45.1% are functioning on a 24×7 basis. Access the state-wise data on functional PHCs and 24×7 PHCs here.
● Under the National Health Mission (NHM), there are a total of 2,423 Advanced Life Support Ambulances, 17,135 Basic Life Support Ambulances, 3,676 Patient Transport Vehicles, 17 boats and 131 bikes across the country.
(To know more about the trends in allocations, releases, and coverage under the scheme, download our 2023 Budget Brief on National Health Mission.)
● Under the National Tele Mental Health Programme, a total of 25 states and Union Territories (UTs) have set up 36 Tele MANAS (Mental Health Assistance and Networking Across States) Cells and have started mental health services. As on 31 January 2023, a total of 43,861 calls have been handled on the helpline number.
Women and Child Health
● Under the PM CARES for children scheme, a total of ₹341.87 crore has been credited to the accounts of 4,345 eligible children.
● Under the One Stop Centre (OSC) scheme, a total of 733 OSCs are currently operational in 36 states and UTs. Based on the impact created by the initiative, GoI will be opening 300 more OSCs in the districts with high rates of Crime Against Women (CAW), preferably in aspirational districts.
● Under the Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 scheme, fortified rice is being actively encouraged in meals as part of the Supplementary Nutrition Program (SNP). In FY 2021-22, a total of 7.3 lakh MT (metric ton) of fortified rice was allocated to various states. Up to the third quarter of FY 2022-23, a total of 9.38 lakh MTs of fortified rice had been allocated to states and UTs. This year onwards fortified rice is being allocated in place of regular rice under the scheme to all states and UTs.
Under Poshan 2.0, Anganwadi Centres (AWCs) are to be strengthened and upgraded to ‘Saksham Anganwadi’. Every year, a target of 40,000 AWCs, out of a total of 2 lakh AWCs, is to be upgraded with the aim of improving health and nutrition services.
As on 31 December 2022, a total of 8.7 crore children in the age group 0-6 years were registered in AWCs across the country. Also, 53 lakh lactating mothers and 68 lakh pregnant mothers have been registered on the Poshan Tracker to avail benefits of POSHAN Abhiyaan, as per Lok Sabha Question answered on 10 February 2023.
(Download our 2023 brief on Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 to know the status and progress of the scheme)
Food Security
● Under National Food Security Act (NFSA), foodgrains will be provided free-of-cost to 80 crore eligible citizens, i.e. to Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY) and Priority Households (PHH), for a period of one year, starting from 1 January 2023.
(To know more about the trends in allocations, releases, and coverage under the scheme, download our 2023 Budget Brief on Food Subsidy and the National Food Security Act.)
To know more about trends in allocations, public expenditures, outputs and outcomes of key social sector programmes, check out our Budget Briefs 2023. This year, we have analysed 12 flagship schemes, and presented a comprehensive overview of India’s welfare system as it has evolved since 2008 as part of our 15th anniversary celebrations. Visit here for a basic overview of the schemes.
Aprajita Verma is a Program Officer at Accountability Initiative.
Glossary
- AB PM-JAY provides health cover of ₹ 5 lakh per family for secondary and tertiary care hospitalisation. The eligibility criteria for eligible households is based on SECC 2011.
- Jal Jeevan Mission is GoI’s rural drinking water programme to provide functional tap connections to every household for drinking, cooking, and other domestic needs on a sustainable basis by 2024.
- In FY 2021-22, GoI restructured the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), POSHAN (Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nourishment) Abhiyaan, and the Scheme for Adolescent Girls (SAG) into Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0.
- National Health Mission (NHM) is GoI’s largest public health programme, which aims to achieve universal access to quality healthcare.
- National Tele Mental Health Programme was launched on 10 October 2022 to improve access to quality mental health counselling and care services in the country.
- As per the NFSA, up to 75% of rural population and 50% of urban population are entitled to receive subsidised foodgrains under Targeted Public Distribution System (TDPS). The AAY households, which constitute the poorest of the poor, are entitled to receive 35 kg of foodgrains per family per month while PHH are entitled to 5 kg per of foodgrains per person per month.
- One Stop Centre scheme, launched in 2015, aims to provide assistance to women affected by violence and who are in distress, through an integrated range of services including medical aid, legal aid, temporary shelter, police assistance, and psycho-social counselling. The OSC scheme falls under the sub-scheme ‘Sambal’ under Mission Shakti.
- PM CARES for Children scheme was launched to support children who lost surviving parents, legal guardians or adoptive parents due to COVID-19 pandemic. The scheme aims to ensure comprehensive care and protection of children, and enable their well being through health insurance, education, and financial support till 23 years of age.
- Poshan Tracker is a mobile based application rolled out by the Ministry of Women and Child Development to enable real-time tracking of the Anganwadi infrastructure and better beneficiary management. Read more here.
- Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana- Gramin (PMAY-G) is GoI’s flagship ‘Housing for All’ scheme. The scheme aims to provide monetary assistance for the construction of a pucca house with basic amenities to all rural houseless families and those living in dilapidated and kutcha houses.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) is Government of India’s (GoI’s) income support scheme, launched in 2019, under which all landholding farmers receive up to ₹6,000 per year to supplement their financial needs.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) is GoI’s crop insurance scheme aimed at providing affordable insurance to ensure comprehensive risk cover against all non-preventable natural risks from pre-sowing to post-harvest stages.
- Pradhan Mantri Poshan Shakti Nirman (PM POSHAN), previously known as the National Programme of Mid-Day Meals in School (MDM), aims to provide one hot cooked meal in government and government-aided schools from FY 2021-22 to FY 2025-26.
- Rural Health Statistics (RHS) 2020-21 report presents a snapshot of Public Health infrastructure & human resources across the country up to 31 March 2021. Read more here.
- Samagra Shiksha is Government of India’s (GoI’s) school education programme covering pre-primary to higher-secondary levels.





