In a Glance: Winter Session 2022
19 January 2022
The Winter Session 2022 of Parliament commenced on 9 December 2022 and was scheduled to conclude on 29 December 2022. The session, however, adjourned sine die six days prior on 23 December 2022. Below are curated highlights from the Question Hour and Zero Hour during the second week of the session (between 19 December 2022 to 23 December 2022), and a brief summary of reports related to welfare schemes.
Highlights from Question Hour and Zero Hour
Health
- According to a Lok Sabha answer, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare stated that the doctor-population ratio in India stands at 1: 834. This was calculated based on the information provided by the National Medical Commission (NMC).
As of June 2022, there were 13,08,009 allopathic doctors registered with the State Medical Councils and the National Medical Commission (NMC) across the country. Additionally, there were 5.65 lakh AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy) doctors in the country. The doctor-population ratio has been calculated by assuming 80% availability of registered allopathic doctors and AYUSH doctors.
Similarly, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare stated that the nurse-population ratio in India stands at 2.06 nurses per 1,000 population. This was calculated based on the information provided by Indian Nursing Council (INC). As on 31 December 2021, there were about 35.14 lakh nursing personnel registered across the country.
- Under the Ayushman Bharat- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), as on 4 December 2022, a total of 20.96 crore beneficiaries have been provided with Ayushman cards. Under the scheme, over 4.18 crore hospital admissions worth ₹48,954.33 crore have been authorised through a network of 26,267 empanelled healthcare providers, including 11,700 private hospitals across the country. State-wise data show that Uttar Pradesh and Bihar account for the highest number of eligible families under the AB-PMJAY at 1.17 crore and 1.08 crore families respectively.
- On the 4th anniversary of Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs), Block Health Melas were organised all across the country between 18-22 April 2022. A total of 4,849 Block Level Health Melas were organised with cumulative footfall of over 47.3 lakh eligible citisens across the country. (Learn more about the Block Health Melas here.)
Women and Child Development
- Under Poshan 2.0, along with local foods and fresh produce, fortified rice and the incorporation of millets at least once a week in meals, has been mandated to tackle anaemia and promote health. During FY 2021-22, a total of 7.34 lakh metric tons of fortified rice (fortified with Iron, Vitamin B-12 and Folic Acid) was allocated to states.
For FY 2022-23, a total of 9.32 metric tons of fortified rice has been allocated to states. A Centrally Sponsored Pilot Scheme has been launched to provide fortified rice to eligible citizens of PM POSHAN, Anganwadi services, and Public Distribution System (PDS) by 2024 in a phased manner. (Download our 2022 briefs on PM POSHAN, and Saksham Anganwadi and POSHAN 2.0 to know the status and progress of the schemes.)
- The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) has launched a portal called ‘GHAR’ – Go Home and Re-Unite for digitally coordinating the repatriation of children under various child protection and welfare schemes.
- There is under-utilisation of funds under the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP) scheme, as highlighted below:
Table 1. Unutilised Funds under BBBP scheme (in ₹ crore)
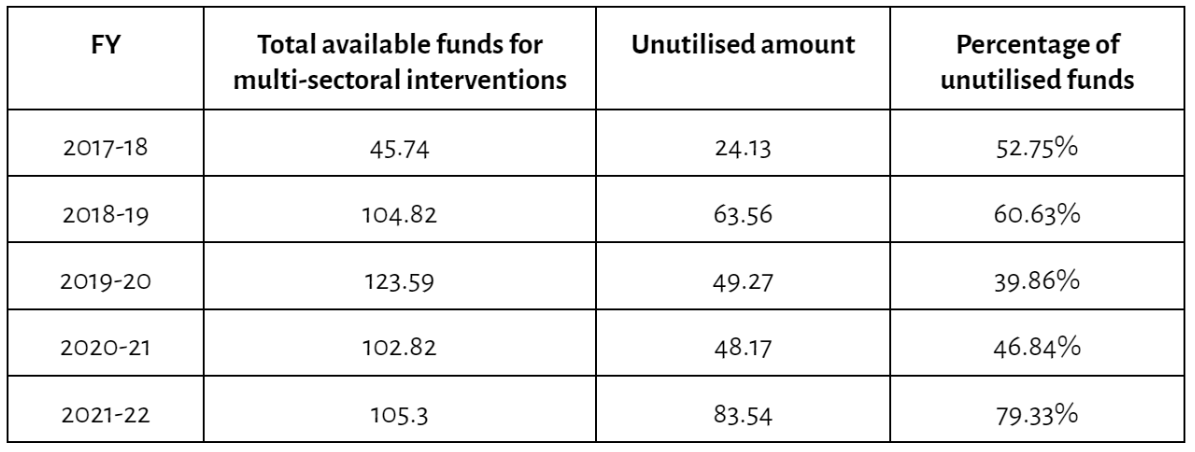
The high percentage of unutilised funds under the BBBP scheme has been attributed to a lack of qualitative initiatives at the level of state and district administration.
Panchayati Raj
- Under the Digital India programme, the Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) is implementing the e-Panchayat Mission Mode Project (MMP). The objective of the mission is to transform the functioning of PRIs (Panchayati Raj Institutions) with ePanchayat initiatives like eGramSwaraj, AuditOnline, and others. Launched in 2020, the eGramSwaraj encompasses all aspects of Panchayat functioning such as budgeting, asset management, monitoring, accounting, etc., on a single digital platform including online payments. In 2022-23, about 2.53 lakh Gram Panchayats (GPs) have prepared and uploaded their Gram Panchayat Development Plans (GPDPs) on eGramSwaraj.
Rural Development
- Under the Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana- Gramin (PMAY-G), as on 15 December 2022, a total of 2.50 crore houses (84.75%) have been sanctioned and construction of 2.11 crore houses (71.5%) have been completed, against the target of 2.95 crore houses by 31st March 2024. (Download our 2022 brief on PMAY-G to know the status and progress of the scheme.)
- On 26 August 2021, the eShram portal was launched by the Ministry of Labour & Employment with the objective of creating a national database of unorganised workers in the country. Initially, the eShram portal was designed with a daily registration capacity of 10-15 lakh per day. However, given the unprecedented response, the daily registration capacity of the portal was enhanced to support 80 lakh registrations per day. Additionally, the Ministry has also onboarded more than 4 lakh Common Service Centres (CSCs) to boost registration on the portal.
- As on 1 December 2022, under the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY), a total road length of 7,98,739 km has been sanctioned and 7,21,362 km (i.e. 90.3%) has been completed.
- While the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) was launched in 2000, new components like PMGSY-I, II, III and Road Connectivity Project for Left Wing Extremism Affected Areas (RCPLWEA) were added subsequently.
The PMGSY-III was launched in 2019 with the aim of consolidating 1,25,000 kms through major rural links by connecting habitations, higher secondary schools, hospitals and Gramin Agricultural Markets (GrAMs). As on 8 December 2022, against the total target, 91,371 km of road length has been sanctioned and 45,946 km has been completed. The implementation period of PMGSY-III is till March 2025.
- The Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP) aims to support rural entrepreneurs in the non-farm sector. It was launched in 2016 as a sub-scheme under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM). As part of the SVEP, a total of 2,21,072 enterprises have been provided support for business development and seed capital through a dedicated Community Enterprise Fund (CEF).
Other
- The One Nation, One Ration Card (ONORC) scheme enables nation-wide portability of benefits under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013. Under the scheme, NFSA beneficiaries can lift foodgrains from any Fair Price Shop (FPS) across the country by using their ration card along with biometric authentication. As on 30 November 2022, a total of 93.31 crore portability transactions have been recorded under the scheme. Out of these, 92.7 crore (99.4%) transactions were intra-state and the remaining 59.64 lakh (0.64%) transactions were inter-state.
- Under the PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi), the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs provides affordable loans to street vendors in three phases: 1st loan of ₹10,000, 2nd loan of ₹20,000, and a 3rd loan of ₹30,000. The implementation of the PM SVANidhi scheme has been extended beyond March 2022 to December 2024.
The scheme aims to provide collateral-free special micro-credit to 42 lakh street vendors by December 2024. As on 30 November 2022, a total of 31.73 lakh street vendors availed the benefit of 1st loan under the scheme. Out of these, 5.81 lakh have availed the benefit of 2nd loan, and 6,926 street vendors have also availed the benefit of 3rd loan.
Highlights from Reports tabled in the Parliament
- The Standing Committee on Labour, Textiles, and Skill Development presented its 36th report titled ‘Implementation of Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojna (PMKVY)’. Launched in 2015, the scheme promotes skill development by providing a variety of industry-relevant skill training courses at the PMKVY Training Centres (TCs) across the country. After successful completion of course mandated assessment and certification, candidates are also provided placement assistance by Training Partners (TPs).
The Committee highlighted the following major trends:
- Under-utilisation of funds under the PMKVY 3.0. In 2021-22, only 72% funds have been utilised under the scheme.
Table 2. Financial Progress of PMKVY 2.0 & PMKVY 3.0 (in ₹ crore)
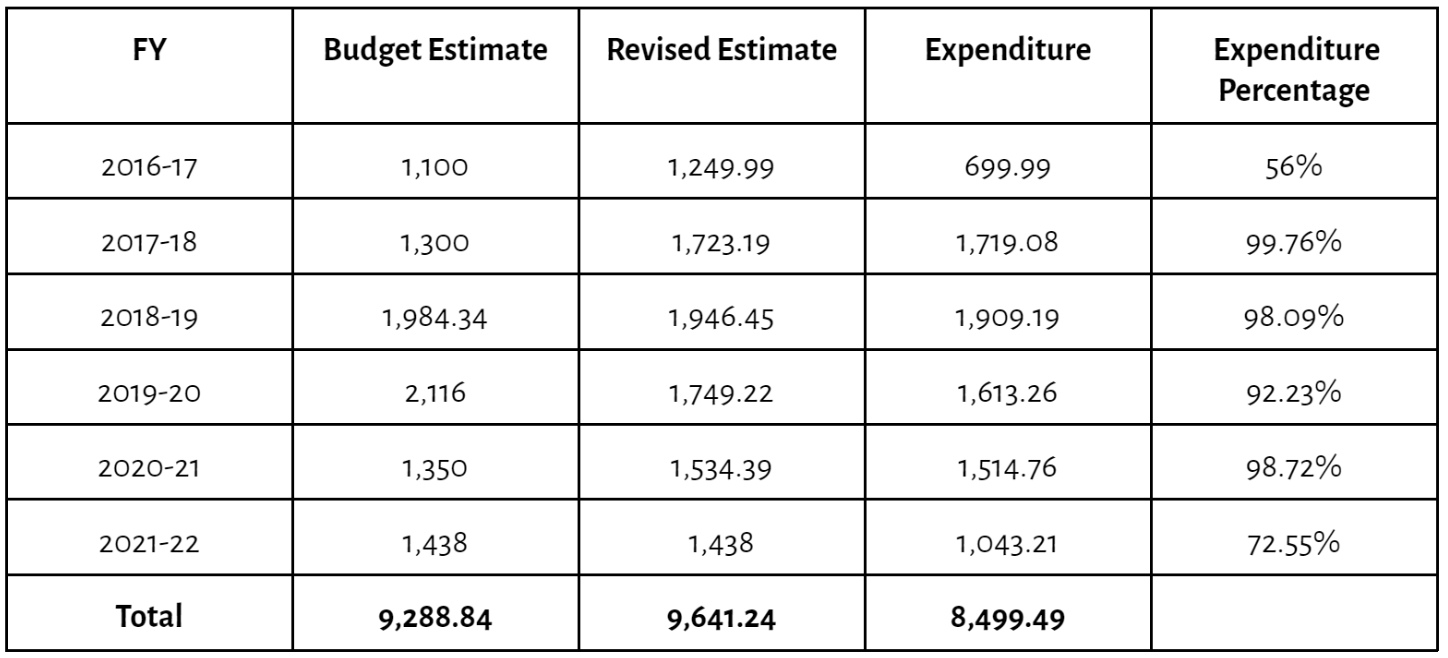
- Out of total enrolment, placement figures for PMKVY 2.0 were low at 23% and PMKVY 3.0 at 8% (up till December 2022 ).
To read the curated highlights of the Budget session 2022 click here, and the Monsoon session 2022 here.





